ポリゴンメッシュで、稜線の一直線上に複数の頂点がある場合に最適化したい (スクリプト)
線形状からポリゴンメッシュに変換した場合など、
面を構成する稜線の一直線上に複数の頂点が含まれる場合があります。
このときに、角を構成する頂点以外を削除して最適化します。
「頂点のクリーン」機能では、削除する頂点のみを選択する必要があります。
以下のスクリプトを実行すると、
ブラウザで選択されたポリゴンメッシュにて、面の稜線の一直線上に複数の頂点がある場合に
頂点を除去し最適化します。
import numpy
import math
scene = xshade.scene()
fMin = 1e-5
# -----------------------------------------------.
# ポリゴンメッシュの面を構成しない頂点や稜線を削除.
# @param[in] shape ポリゴンメッシュクラス.
# -----------------------------------------------.
def cleanupPolygonmesh (shape):
# 面で参照される頂点を取得.
versCou = shape.total_number_of_control_points
facesCou = shape.number_of_faces
vUsedList = [0] * versCou
for fLoop in range(facesCou):
f = shape.face(fLoop)
vCou = f.number_of_vertices
for i in range(vCou):
vUsedList[ f.vertex_indices[i] ] = 1
# 参照されない頂点を削除.
shape.begin_removing_control_points()
for i in range(versCou):
if vUsedList[i] == 0:
shape.remove_control_point(i)
shape.end_removing_control_points()
shape.update()
# -----------------------------------------------.
# 面の頂点のうち、一番3点が作る角度が大きい頂点を取得.
# @param[in] faceD ポリゴンメッシュクラス.
# -----------------------------------------------.
def getMaxAngleInFace (faceD):
vCou = faceD.number_of_vertices
if vCou <= 2:
return -1
maxIndex = -1
maxAngle = 1.0
for i in range(vCou):
prevV = shape.vertex(faceD.vertex_indices[(i - 1 + vCou) % vCou]).position
curV = shape.vertex(faceD.vertex_indices[i]).position
nextV = shape.vertex(faceD.vertex_indices[(i + 1) % vCou]).position
prevV = numpy.array([prevV[0], prevV[1], prevV[2]])
curV = numpy.array([curV[0], curV[1], curV[2]])
nextV = numpy.array([nextV[0], nextV[1], nextV[2]])
lenV1 = numpy.linalg.norm(curV - prevV)
if lenV1 < fMin:
continue
lenV2 = numpy.linalg.norm(nextV - curV)
if lenV2 < fMin:
continue
dirV1 = (prevV - curV) / lenV1
dirV2 = (nextV - curV) / lenV2
cAngleV = math.fabs(numpy.dot(dirV1, dirV2))
if maxIndex < 0 or (cAngleV < maxAngle and cAngleV < 0.999):
maxIndex = i
maxAngle = cAngleV
if maxIndex < 0:
maxIndex = 0
return maxIndex
# -----------------------------------------------.
# 指定の面の頂点を指定して追加.
# UVやfaceGroup、頂点カラーについても考慮.
# @param[in] shape ポリゴンメッシュクラス.
# @param[in] faceIndex 面番号.
# @param[in] indicesList 面の頂点インデックス。-1の場合は面の頂点を削除する.
# -----------------------------------------------.
def appendNewFace (shape, faceIndex, indicesList):
vCou = len(indicesList)
if vCou < 3:
return False
uvLayersCou = shape.get_number_of_uv_layers()
vertexColorCou = shape.number_of_vertex_color_layers
f = shape.face(faceIndex)
faceGroupIndex = shape.get_face_group_index(faceIndex)
# 新しい面の頂点インデックス.
newFaceV = []
for i in range(vCou):
if indicesList[i] >= 0:
newFaceV.append(indicesList[i])
# 新しい面のUV.
newFaceUVs = []
for i in range(uvLayersCou):
uvs = []
for j in range(vCou):
if indicesList[j] >= 0:
uvs.append(f.get_face_uv(i, j))
newFaceUVs.append(uvs)
# 新しい面の頂点カラー.
newFaceColors = []
for i in range(vertexColorCou):
colors = []
for j in range(vCou):
if indicesList[j] >= 0:
colors.append(f.get_vertex_color(i, j))
newFaceColors.append(colors)
if len(newFaceV) < 2:
return False
# polygon_meshに面情報を追加.
newFaceIndex = shape.number_of_faces
shape.append_face(newFaceV)
newF = shape.face(newFaceIndex)
newVCou = newF.number_of_vertices
for i in range(uvLayersCou):
uvs = newFaceUVs[i]
for j in range(newVCou):
newF.set_face_uv(i, j, uvs[j])
for i in range(vertexColorCou):
colors = newFaceColors[i]
for j in range(newVCou):
newF.set_vertex_color(i, j, colors[j])
shape.set_face_group_index(newFaceIndex, faceGroupIndex)
return True
# -----------------------------------------------.
# 指定のポリゴンメッシュで、面ごとに直線上の頂点を取得.
# -----------------------------------------------.
def cleanupMeshVertices (shape):
if shape.type != 7: # ポリゴンメッシュでない場合.
return None
versCou = shape.total_number_of_control_points
facesCou = shape.number_of_faces
removeFaceList = []
# 各頂点が共有する面の数を保持.
verFacesCouList = [0] * versCou
for fLoop in range(facesCou):
f = shape.face(fLoop)
vCou = f.number_of_vertices
for i in range(vCou):
vIndex = f.vertex_indices[i]
verFacesCouList[vIndex] += 1
for fLoop in range(facesCou):
f = shape.face(fLoop)
# 角のある頂点を取得.
maxVIndex = getMaxAngleInFace(f)
if maxVIndex < 0:
removeFaceList.append(fLoop)
continue
# 面で削除する頂点番号を保持.
vCou = f.number_of_vertices
chkF = False
fVIndexList = [0] * vCou
for i in range(vCou):
fVIndexList[i] = f.vertex_indices[i]
vIndex0 = maxVIndex
for i in range(vCou):
vIndex1 = (maxVIndex + i + 1 + vCou) % vCou
vI1 = f.vertex_indices[vIndex1]
p0 = shape.vertex(f.vertex_indices[vIndex0]).position
p1 = shape.vertex(vI1).position
p0 = numpy.array([p0[0], p0[1], p0[2]])
p1 = numpy.array([p1[0], p1[1], p1[2]])
lenV = numpy.linalg.norm(p1 - p0)
if lenV < fMin:
fVIndexList[vIndex1] = -1
chkF = True
continue
vIndex2 = (maxVIndex + i + 2 + vCou) % vCou
p2 = shape.vertex(f.vertex_indices[vIndex2]).position
p2 = numpy.array([p2[0], p2[1], p2[2]])
lenV2 = numpy.linalg.norm(p2 - p1)
if lenV2 < fMin:
fVIndexList[vIndex1] = -1
chkF = True
continue
vDir1 = (p1 - p0) / lenV
vDir2 = (p2 - p1) / lenV2
cAngleV = math.fabs(numpy.dot(vDir1, vDir2))
if cAngleV > 0.99 and verFacesCouList[vI1] <= 2:
fVIndexList[vIndex1] = -1
chkF = True
continue
vIndex0 = vIndex1
# 新しく面を追加.
if chkF:
appendNewFace(shape, fLoop, fVIndexList)
removeFaceList.append(fLoop)
if len(removeFaceList) > 0:
shape.make_edges()
shape.update()
# 古い面を削除.
shape.begin_removing_faces()
for fIndex in removeFaceList:
shape.remove_face(fIndex)
shape.end_removing_faces()
shape.update()
# 面から参照されない頂点を削除.
cleanupPolygonmesh(shape)
return shape
# -------------------------------------------------.
# 選択されたポリゴンメッシュの頂点を最適化.
# -------------------------------------------------.
newShapesList = []
for shape in scene.active_shapes:
nShape = cleanupMeshVertices(shape)
if nShape != None:
newShapesList.append(nShape)
if len(newShapesList) == 0:
print 'ポリゴンメッシュを選択してください。'
else:
scene.active_shapes = newShapesList
使い方
以下のような、ポリゴンメッシュの面で頂点が直線上に複数並んでいる形状があるとします。
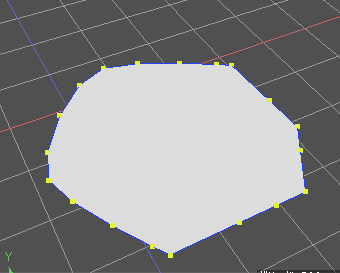
これをブラウザで選択し、上記のスクリプトを実行します。
頂点の選択は不要です。
複数ポリゴンメッシュを選択してまとめて対応できます。
以下のように、一直線上にある頂点が整理され頂点が削減されました。
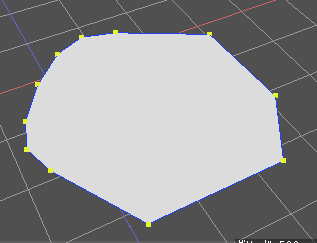
このスクリプトでは、頂点/UV/フェイスグループ/頂点カラーが最適化で考慮されます。
なお、UNDO/REDOには対応していません。
また、形状によっては頂点が最適化されることにより、わずかに輪郭が変化する場合があります。
これは上記スクリプトのcleanupMeshVertices内の
「if cAngleV > 0.99」の数値を「0.999」など1.0に近づけることで精度を上げることができます。