6面に分離されたキューブマップテクスチャをファイル出力したい (スクリプト)
WebGLなどでHDRを使ったIBL用の映り込みや背景の表示を行う場合、
6面の分離されたキューブマップテクスチャを使用します。
別途、WebGLのフレームワークによってはパノラマの1枚の画像を使用してShaderで表現する手段もあります。
ここではスクリプトを使用し、
カメラを中心にバーティカルクロス形式でレンダリングした後に
そのテクスチャより6枚分のキューブマップテクスチャをファイル出力します。
以下のスクリプトを実行すると、
カメラを中心にレンダリングが行われます。
このとき、元のレンダリングサイズとレンダリングイメージは上書きされるためご注意くださいませ。
レンダリング後、指定のフォルダにキューブマップテクスチャに展開されたイメージが出力されます。
scene = xshade.scene()
# ------------------------------------------------------------.
# レンダリングを行う.
# 左右上下1ピクセルごとのマージンを設けてレンダリング.
# @param[in] cubeSize キューブマップのサイズ (512, 1024 など).
# ------------------------------------------------------------.
def doRendering (cubeSize):
# レンダリングサイズ.
renderWidth = (cubeSize + 2) * 3
renderHeight = (cubeSize + 2) * 4
scene.rendering.image_size = [renderWidth, renderHeight]
# バーティカルクロスのパノラマ投影.
scene.rendering.panorama_projection = 5
# レンダリング.
# レンダリングが完了するまで待つ.
scene.rendering.render()
# ------------------------------------------------------------.
# 指定の名前のマスターイメージを取得.
# ------------------------------------------------------------.
def findMasterImageByName (nameStr):
# マスターイメージパートを取得.
shape = scene.shape
masterImagePart = None
if shape.has_son:
s = shape.son
while s.has_bro:
s = s.bro
if s.type == 2 and s.part_type == 102: # マスターイメージパート.
masterImagePart = s
break
if masterImagePart == None or masterImagePart.has_son == False:
return None
# マスターイメージ内で指定の名称があるか.
targetShape = None
s = masterImagePart.son
while s.has_bro:
s = s.bro
if s.name == nameStr:
targetShape = s
break
return targetShape
# ------------------------------------------------------------.
# キューブマップレンダリング結果を6つのマスターイメージとして分離.
# @param[in] outputPath ファイルにキューブマップ画像を出力する場合のパス.
# @param[in] outputFileType ファイル拡張子.
# ------------------------------------------------------------.
def createCubeTextures (outputPath, outputFileType):
if scene.rendering.image == None or scene.rendering.image.has_image == False:
return
width = scene.rendering.image.size[0]
height = scene.rendering.image.size[1]
orgTexWidth = width / 3
orgTexHeight = height / 4
cubeTexWidth = orgTexWidth - 2
cubeTexHeight = orgTexHeight - 2
cubeTexName = ['cubeTex_px','cubeTex_nx','cubeTex_py','cubeTex_ny','cubeTex_pz','cubeTex_nz']
cubePosA = [ (orgTexWidth * 2, orgTexHeight), (0, orgTexHeight),
(orgTexWidth, 0), (orgTexWidth, orgTexHeight * 2),
(orgTexWidth, orgTexHeight * 3), (orgTexWidth, orgTexHeight) ]
# 色補正を行うか.
useColorCorrection = False
if outputFileType != 'exr':
useColorCorrection = True
for i in range(6):
xPos = cubePosA[i][0] + 1
yPos = cubePosA[i][1] + 1
# cubeTexName[i]の名前のマスターイメージが存在するか.
masterImage = findMasterImageByName(cubeTexName[i])
if masterImage == None:
masterImage = scene.create_master_image(cubeTexName[i])
masterImage.image = xshade.create_image((cubeTexWidth, cubeTexHeight), 128)
for y in range(cubeTexHeight):
for x in range(cubeTexWidth):
# レンダリング画像上のピクセル色を取得.
if i == 4: # pzの場合は左右と上下を逆にする.
col = scene.rendering.image.get_pixel_rgba(cubeTexWidth + xPos - x, cubeTexHeight + yPos - y)
else:
col = scene.rendering.image.get_pixel_rgba(x + xPos, y + yPos)
# 色補正を行う.
col2 = col
if useColorCorrection:
col2 = scene.correction.correct([col[0], col[1], col[2]])
# 色をmasterImage.imageに指定.
masterImage.image.set_pixel_rgba(x, y, [col2[0], col2[1], col2[2], col[3]])
# ファイル出力.
if outputPath != '':
fName = outputPath + '/' + cubeTexName[i] + '.' + outputFileType
masterImage.image.save(fName)
# ----------------------------------------------------------.
# ダイアログボックスの作成.
dlg = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid('51cbd867-c363-47f9-9741-7afa5a4e48ed')
cubeTexSize_id = dlg.append_selection('キューブマップサイズ : /256/512/1024/2048/4096', '')
outputImageFile_id = dlg.append_bool('イメージをファイル出力')
outputFilePath_id = dlg.append_path('出力フォルダ : ')
outputFileType_id = dlg.append_selection('出力イメージ形式 : /jpg/png/exr', '')
# デフォルトボタンを追加.
dlg.append_default_button()
# 値を指定.
dlg.set_value(cubeTexSize_id, 1)
dlg.set_value(outputImageFile_id, True)
dlg.set_value(outputFileType_id, 0)
# デフォルト値を指定.
dlg.set_default_value(cubeTexSize_id, 1)
dlg.set_default_value(outputImageFile_id, True)
dlg.set_default_value(outputFileType_id, 0)
# ダイアログボックスを表示.
if dlg.ask('キューブマップテクスチャを出力'):
# ダイアログボックスでの値を取得.
tSizeA = [256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096]
cubeTexSize = tSizeA[dlg.get_value(cubeTexSize_id)]
outputImageFile = dlg.get_value(outputImageFile_id)
fTypeA = ['jpg', 'png', 'exr']
outputFileType = fTypeA[dlg.get_value(outputFileType_id)]
outputPath = dlg.get_value(outputFilePath_id)
if outputImageFile == False:
outputPath = ''
if outputImageFile and outputPath == '':
print 'キューブマップテクスチャを出力するパスを指定してください。'
else:
# キューブマップレンダリングを行う.
doRendering(cubeTexSize)
# キューブマップレンダリング結果を6つのマスターイメージとして分離.
createCubeTextures(outputPath, outputFileType)
print 'キューブマップテクスチャを出力しました。'
if outputPath != '':
print 'キューブマップテクスチャを [' + outputPath + '] に出力しました。'
使い方
あらかじめ背景とするイメージや形状をシーンに配置します。
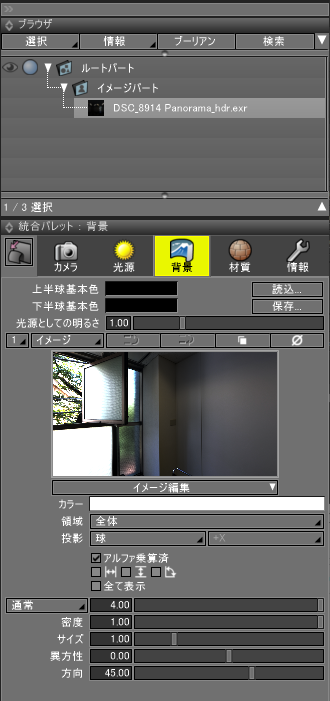
上記のスクリプトをコピーし、Shade3Dのスクリプトウィンドウにペーストします。
実行すると以下のようなダイアログボックスが表示されます。
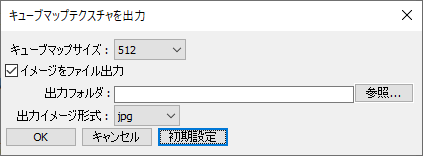
「キューブマップサイズ」は、出力するキューブマップの解像度です。
256/512/1024/2048/4096から選択できます。
「イメージをファイル出力」チェックボックスをオンにすると、指定のフォルダにキューブマップテクスチャを出力します。
オフにすると、マスターイメージとしてシーンにキューブマップテクスチャが保持されるだけになります。
「出力フォルダ」の「参照」ボタンを押し、キューブマップテクスチャを出力するフォルダを指定します。
「出力イメージ形式」は、jpg/png/exrから選択できます。
jpg/png形式で出力する場合は色補正が反映されます。exrの場合は、そのままのレンダリング色が反映されます。
「OK」ボタンを押すと、
レンダリングとキューブマップテクスチャのマスターイメージ展開、ファイル出力が行われます。
これはキューブマップサイズが大きい場合は時間がかかります。
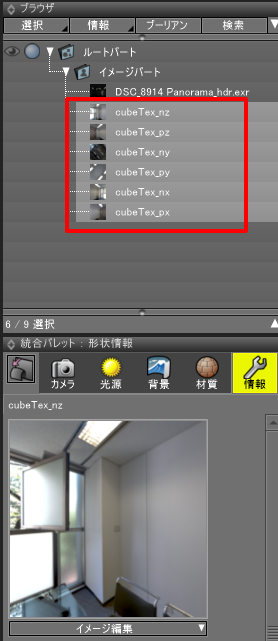
マスターイメージは以下のようにイメージパートに展開されます。
「イメージをファイル出力」チェックボックスをオンにしている場合、以下のように指定のフォルダにファイルが出力されます。
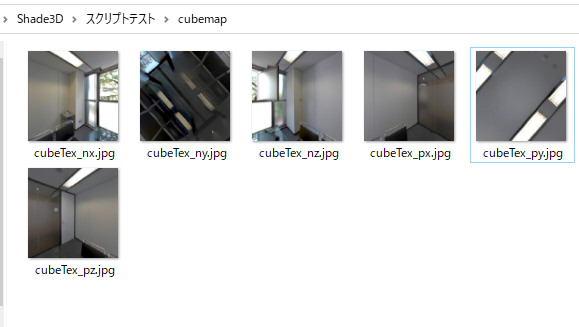
出力されたキューブマップテクスチャの名前
6枚のテクスチャは以下のような内容になっています。
| 出力名 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| cubeTex_nx | -X |
| cubeTex_px | +X | cubeTex_ny | -Y |
| cubeTex_py | +Y | cubeTex_nz | -Z |
| cubeTex_pz | +Z |
出力するキューブマップサイズの注意事項
Shade3Dのグレードにより、レンダリングできる解像度の上限が異なります。
レンダリング画像サイズの最大がBasicは2500 x 2500、Standardは4500 x 4500、Professionalは22528 x 22528となります。
そのため、このキューブマップ出力スクリプトを使ったときのキューブマップサイズは
Basic版では最大512、Standard版では最大1024、となります。
Professional版の場合は4096も指定可能です。
キューブマップの場合は6面で構成されるため、1024を指定した場合は4K解像度の背景(1024 x 4で周囲ぐるっと360度分)に相当します。
WebGL(three.js)で使用する場合
出力されたキューブマップテクスチャをWebGLで使用する場合は、環境によっては少し調整が必要になります。
three.js ( https://threejs.org/ )で使用する場合は、
キューブマップのnzとpzは逆にするようにしてください。
以下はWebGL(three.js)でのブラウザでの表示例です。
