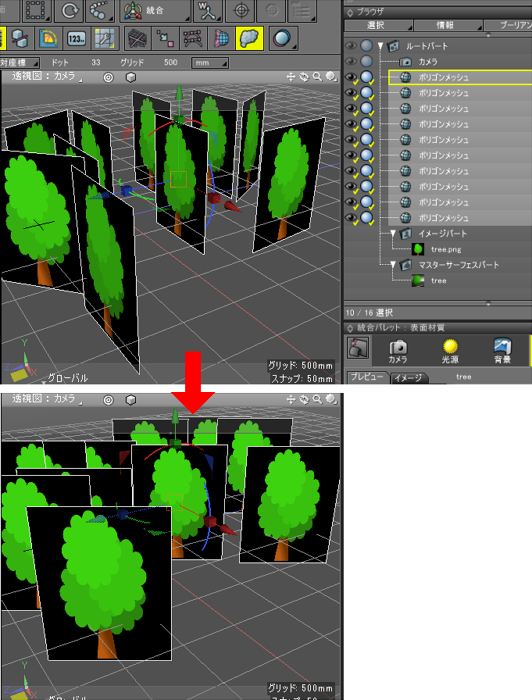
指定の形状が視線方向を向くようにしたい (スクリプト)
スクリプトを使用して、指定の形状が視線方向を向くように計算/再配置します。
Standard/Professionalのグレードの場合は「エイムコンストレインツ」を使用することで、
指定の形状がカメラを向くように連動させることができます。
エイムコンストレインツは、Standard/Professionalのグレードでのみ使用できる機能です。
Basicでは利用できませんが
スクリプトを使用することで、指定の形状を特定の形状に向かせる計算を行います。
カメラの視点と注視点のワールド座標位置は、「カメラのワールド座標での視点と注視点を知りたい (スクリプト)」のスクリプトより取得できます。
この時取得できる視点と注視点が作る方向ベクトルを用い、
ブラウザで選択されたポリゴンメッシュのはじめの面の法線を視線方向に向かせるものとします。
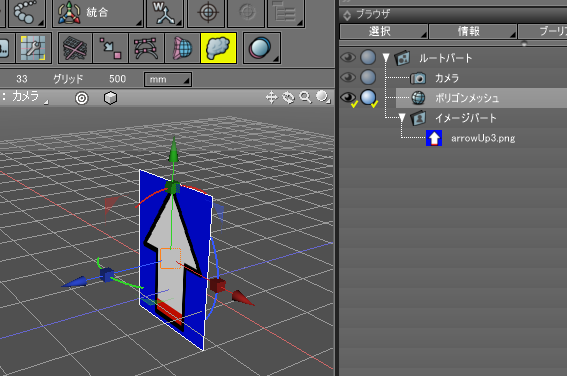
また、2つのベクトルが作る回転行列の計算として「2つのベクトルが作る回転行列を計算 (スクリプト)」の記載を使用しています。
スクリプト全体は以下になります。
import numpy
import math
scene = xshade.scene()
#---------------------------------------.
# ゼロチェック.
# @param[in] v 実数値.
# @return ゼロの場合はTrue.
#---------------------------------------.
def isZero (v):
minV = 1e-5
if v > -minV and v < minV:
return True
return False
#---------------------------------------.
# ベクトルの長さを計算.
# @param[in] v ベクトル値.
# @return ベクトルの長さ.
#---------------------------------------.
def length_vec3 (v):
vec3 = numpy.array(v)
return numpy.linalg.norm(vec3)
#---------------------------------------.
# 単位ベクトルを計算.
# @param[in] v xyzのベクトル値.
# @return 正規化されたベクトル値.
#---------------------------------------.
def normalize_vec3 (v):
vec3 = numpy.array(v)
len = numpy.linalg.norm(vec3)
if isZero(len):
return [0, 0, 0]
return vec3 / len
#---------------------------------------.
# 単位ベクトルを計算.
# @param[in] v xyzwのベクトル値.
# @return 正規化されたベクトル値.
#---------------------------------------.
def normalize_vec4 (v):
vec4 = numpy.array(v)
len = numpy.linalg.norm(vec4)
if isZero(len):
return [0, 0, 0, 0]
return vec4 / len
#---------------------------------------.
# 内積を計算.
# @param[in] v1 xyzのベクトル1.
# @param[in] v2 xyzのベクトル2.
# @return 内積の値.
#---------------------------------------.
def dot_vec3 (v1, v2):
vec3_1 = numpy.array(v1)
vec3_2 = numpy.array(v2)
return numpy.dot(vec3_1, vec3_2)
#---------------------------------------.
# 外積を計算.
# @param[in] v1 xyzのベクトル1.
# @param[in] v2 xyzのベクトル2.
# @return 外積のベクトル.
#---------------------------------------.
def cross_vec3 (v1, v2):
vec3_1 = numpy.array(v1)
vec3_2 = numpy.array(v2)
return numpy.cross(vec3_1, vec3_2)
#---------------------------------------.
# ベクトルaをbに向かせるquaternionを求める.
# @param[in] a xyzのベクトル1.
# @param[in] b xyzのベクトル2.
# @return Quaternion値.(w,x,y,z)として入っている.
#---------------------------------------.
def quaternion_a_b (a, b):
a = normalize_vec3(a)
b = normalize_vec3(b)
q = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
c = cross_vec3(b, a)
d = -length_vec3(c)
c = normalize_vec3(c)
epsilon = 0.0002
ip = dot_vec3(a, b)
if -epsilon < d or 1.0 < ip:
if ip < (epsilon - 1.0):
a2 = [-a[1], a[2], a[0]]
c = normalize_vec3(cross_vec3(a2, a))
q[0] = 0.0
q[1] = c[0]
q[2] = c[1]
q[3] = c[2]
else:
q = numpy.array([1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
else:
e = c * math.sqrt(0.5 * (1.0 - ip))
q[0] = math.sqrt(0.5 * (1.0 + ip))
q[1] = e[0]
q[2] = e[1]
q[3] = e[2]
return q
#---------------------------------------.
# quaternionから4x4行列を求める.
# @param[in] quaternion値。(w,x,y,z)として入っている.
# @return 4x4の回転行列.
#---------------------------------------.
def quaternion_matrix4x4 (q):
m = numpy.matrix(numpy.identity(4))
# q(w,x,y,z)から(x,y,z,w)に並べ替え.
q2 = range(4)
q2[0] = q[1]
q2[1] = q[2]
q2[2] = q[3]
q2[3] = q[0]
m[0,0] = q2[3]*q2[3] + q2[0]*q2[0] - q2[1]*q2[1] - q2[2]*q2[2]
m[0,1] = 2.0 * q2[0] * q2[1] - 2.0 * q2[3] * q2[2]
m[0,2] = 2.0 * q2[0] * q2[2] + 2.0 * q2[3] * q2[1]
m[0,3] = 0.0
m[1,0] = 2.0 * q2[0] * q2[1] + 2.0 * q2[3] * q2[2]
m[1,1] = q2[3] * q2[3] - q2[0] * q2[0] + q2[1] * q2[1] - q2[2] * q2[2]
m[1,2] = 2.0 * q2[1] * q2[2] - 2.0 * q2[3] * q2[0]
m[1,3] = 0.0
m[2,0] = 2.0 * q2[0] * q2[2] - 2.0 * q2[3] * q2[1]
m[2,1] = 2.0 * q2[1] * q2[2] + 2.0 * q2[3] * q2[0]
m[2,2] = q2[3] * q2[3] - q2[0] * q2[0] - q2[1] * q2[1] + q2[2] * q2[2]
m[2,3] = 0.0
m[3,0] = 0.0
m[3,1] = 0.0
m[3,2] = 0.0
m[3,3] = q2[3] * q2[3] + q2[0] * q2[0] + q2[1] * q2[1] + q2[2] * q2[2]
k = m[3,3]
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
m[i,j] /= k
m[3,3] = 1.0
return m
#---------------------------------------.
# ベクトルaをbに向かせる回転行列を求める.
# @param[in] _a xyzのベクトル1.
# @param[in] _b xyzのベクトル2.
# @return 4x4の回転行列.
#---------------------------------------.
def rotate_a_to_b_matrix4x4 (_a, _b):
m = numpy.matrix(numpy.identity(4))
a = numpy.array([_a[0], _a[1], _a[2]])
b = numpy.array([_b[0], _b[1], _b[2]])
return quaternion_matrix4x4( quaternion_a_b(a, b) )
#---------------------------------------.
# カメラの視点と注視点を計算.
#---------------------------------------.
# ローカル座標でのカメラの位置と注視点.
eye = scene.camera.eye
target = scene.camera.target
# カメラのローカル・ワールド変換行列.
lwMat = numpy.matrix(numpy.identity(4))
if scene.camera.camera_object != None:
lwMat = numpy.matrix(scene.camera.camera_object.local_to_world_matrix)
# カメラの位置と注視点をワールド座標に変換.
eye = numpy.dot(numpy.array([eye[0], eye[1], eye[2], 1.0]), lwMat)
target = numpy.dot(numpy.array([target[0], target[1], target[2], 1.0]), lwMat)
eye = [eye[0,0], eye[0,1], eye[0,2]]
target = [target[0,0], target[0,1], target[0,2]]
# 視線ベクトルを計算.
eyeDir = numpy.array([target[0], target[1], target[2]]) - numpy.array([eye[0], eye[1], eye[2]])
eyeDir = normalize_vec3(eyeDir)
# -----------------------------------------------.
# shapeの形状の、面0のワールド座標での法線を取得.
# -----------------------------------------------.
def getFace0Normal (shape, lwMat):
shape.setup_normal() # 法線を計算.
if shape.number_of_faces == 0:
return [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
# 面の法線.
pV = shape.get_plane_equation(0)
normal = numpy.array([pV[0], pV[1], pV[2], 0.0])
# ワールド座標に変換.
m = numpy.matrix(lwMat)
wNormal = numpy.dot(normal, m)
return [wNormal[0,0], wNormal[0,1], wNormal[0,2]]
# -----------------------------------------------.
# shapeの形状の、面0のワールド座標での中心を取得.
# -----------------------------------------------.
def getFace0Center (shape, lwMat):
center = numpy.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0])
if shape.number_of_faces == 0:
return [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
face = shape.face(0)
indices = face.vertex_indices
num = len(indices)
for i in range(num):
p = shape.vertex(indices[i]).position
center += numpy.array([p[0], p[1], p[2], 0.0])
center /= float(num)
# ワールド座標に変換.
m = numpy.matrix(lwMat)
wCenter = numpy.dot(center, m)
return [wCenter[0,0], wCenter[0,1], wCenter[0,2]]
# -----------------------------------------------.
# 指定の位置を中心にポリゴンメッシュを回転.
# @param[in] shape 対象のポリゴンメッシュ形状.
# @param[in] wCenterPos 回転のワールド座標での中心位置.
# @param[in] rotM 回転の4x4行列.
# -----------------------------------------------.
def rotatePolygonMesh (shape, wCenterPos, rotM):
if shape.type != 7: # ポリゴンメッシュではない場合.
return
# ローカルからワールド座標に変換する行列.
lwMat = numpy.matrix(shape.local_to_world_matrix)
# ワールドからローカル座標に変換する行列.
wlMat = numpy.matrix(shape.world_to_local_matrix)
# rotMをnumpyの4x4行列に変換.
nRotM = numpy.matrix(rotM)
versCou = shape.total_number_of_control_points
for i in range(versCou):
# 頂点をワールド座標で取得.
p = shape.vertex(i).position
wPos = numpy.array([p[0], p[1], p[2], 1.0])
m = numpy.dot(wPos, lwMat)
wPos[0] = m[0,0]
wPos[1] = m[0,1]
wPos[2] = m[0,2]
# wCenterPos中心でrotMの回転行列で座標変換.
v4 = numpy.array([wPos[0] - wCenterPos[0], wPos[1] - wCenterPos[1], wPos[2] - wCenterPos[2], 1.0])
m = numpy.dot(v4, nRotM)
wPos[0] = m[0,0] + wCenterPos[0]
wPos[1] = m[0,1] + wCenterPos[1]
wPos[2] = m[0,2] + wCenterPos[2]
# ローカル座標に変換.
v4 = numpy.array([wPos[0], wPos[1], wPos[2], 1.0])
m = numpy.dot(v4, wlMat)
# 計算後の頂点を格納.
shape.vertex(i).position = [m[0,0], m[0,1], m[0,2]]
# -----------------------------------------------.
# ブラウザで選択された形状がポリゴンメッシュの場合、向きを視線方向にする.
# -----------------------------------------------.
for shape in scene.active_shapes:
if shape.type == 7: # ポリゴンメッシュ.
shape.setup_normal() # 法線を計算.
if shape.number_of_faces == 0:
continue;
# ローカルからワールド座標に変換する行列.
lwMat = shape.local_to_world_matrix
# 面0の法線.
normal = getFace0Normal(shape, lwMat)
# 面0のワールド座標での中心.
centerV = getFace0Center(shape, lwMat)
# normalをeyeDirに向かせるための回転行列を計算.
rotM = rotate_a_to_b_matrix4x4(normal, -eyeDir)
# shapeのポリゴンメッシュを、centerVを中心にrotMの回転行列で回転させる.
rotatePolygonMesh(shape, centerV, rotM)
実行結果は以下のようになります。
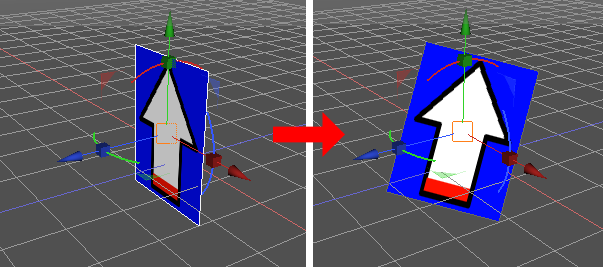
Y軸固定で回転
Y軸固定で木のビルボードのように回転させる場合は、以下のスクリプトになります。
視点/注視点の計算、ベクトル/行列計算の関数などは上記のスクリプトを再利用しました。
# -----------------------------------------------.
# ブラウザで選択された形状がポリゴンメッシュの場合、向きを視線方向にする.
# -----------------------------------------------.
# eyeDirのY成分を0にする.
eyeDir[1] = 0.0
eyeDir = normalize_vec3(eyeDir)
for shape in scene.active_shapes:
if shape.type == 7: # ポリゴンメッシュ.
shape.setup_normal() # 法線を計算.
if shape.number_of_faces == 0:
continue;
# ローカルからワールド座標に変換する行列.
lwMat = shape.local_to_world_matrix
# 面0の法線.
normal = getFace0Normal(shape, lwMat)
# Y成分を0にする.
normal[1] = 0.0
normal = normalize_vec3(normal)
# 面0のワールド座標での中心.
centerV = getFace0Center(shape, lwMat)
# normalをeyeDirに向かせるための回転行列を計算.
rotM = rotate_a_to_b_matrix4x4(normal, -eyeDir)
# shapeのポリゴンメッシュを、centerVを中心にrotMの回転行列で回転させる.
rotatePolygonMesh(shape, centerV, rotM)
実行結果は以下のようになります。
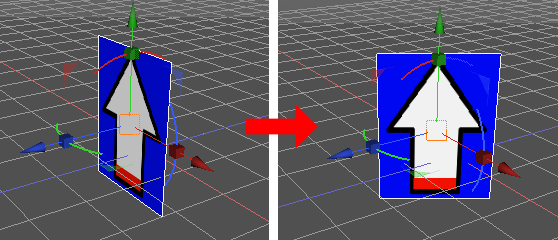
このスクリプトは、以下の画像のように
ビルボードの木をカメラ方向にまとめて向かせる場合などに利用できます。